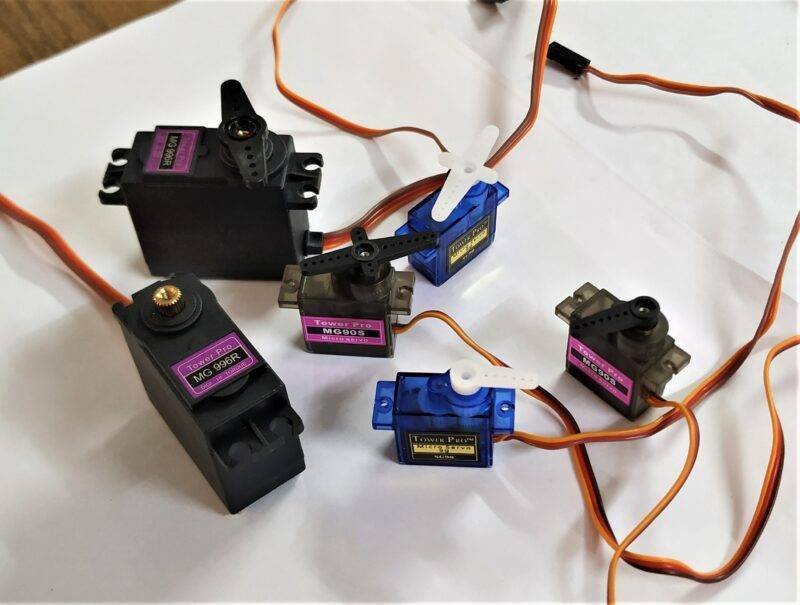
Hello Techies, welcome back to another amazing tutorial on “Working of Servo motors using Arduino “. The tutorial is going to be useful in case u want to know
- What are Servo motors and their applications?
- Working of Servo motors?
- Servo motor connection with Arduino.

What is Servo motor and its applications?
Servo motors are used in every joint to perform precise angular movements. Today in the era of industry 4.0, we are using servo motors heavily, to meet the increasing demands of commercialization and industrialization. They are majorly used in sectors like:
- In heavy Robotic Vehicles
- In metal cutting and forming the machinery
- In Antenna positioning etc.
WHY?
- They are in general, high efficiency and great precision operational motors. They can easily turn to specified positions, using the positional feedback system discussed below.
- The servo arm maximum turn limit is 180 degrees and by connecting the servo with Arduino, one can control the position of servo motors.
- A servo system is a closed-loop system where the feedback signal (output signal) in parameters like position, velocity, acceleration, etc. drives the motor. It converts the feedback electric signals to angular velocity or angular position.

Assembly:
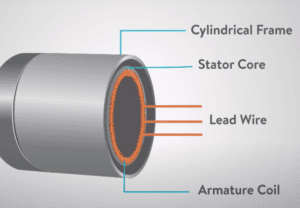
Servo motors are the part of closed-loop systems in which the control unit, amplifier, shaft, encoder and servo motor all are connected in a loop with each other.

Note: Servo Motors are nothing but a regular DC motor coupled with a sensor to provide positional feedback or feedback signal.
- It is controlled by analog and digital types of electric signals.
- It has three types of classifications – AC or DC servo motors, Brushed or Brushless motors, and Synchronous or Asynchronous motors.
- AC or DC servo motors are categorized based on the “types of currents“, they operate. AC servo motors withstand higher currents and are mostly used where high repetition and precision are required whereas, DC servo is mostly used to carry fewer loads.
- Brushed or Brushless servo motors are categorized based on “types of commutators“, they are designed of. Brushed motors are simple and easy to rotate with noise whereas brushless are used to achieve higher efficiency with less noise.
- Synchronous or Asynchronous servo motors are categorized based on “types of magnetic field“ produced inside armature. The motors have two types of coils inside namely the Stator armature coil and the Rotor armature coil.

| 1. | Synchronous | Stator speed = Rotor Speed | The magnetic field produced for both are the same |
| 2. | Asynchronous | Stator speed > Rotor speed | The magnetic field produced for both are different |
Working of Servo motors?
*Servo Motor = DC Motor + Gear Assembly + Position sensing device*
- PLC motion controller from the control unit generates the electric pulses, which is fed to the DC Motor.
- As a result, the motor rotates as per the voltage applied through the pulses.
- Corresponding to the angular velocity of the motor shaft and gear mechanism, voltage is produced as a feedback signal which is sensed using a sensing device. Here we are describing the servo motor working.
The voltage produced is again fed back to the control unit and the comparator finds the error as
ERROR= Output voltage (feedback signal)- Input Voltage(fed signal) .
The error when applied back to the DC motor armature results in amplification of the input, and the motor moves with a more powerful speed. Now,
KEY POINTS TO REMEMBER:
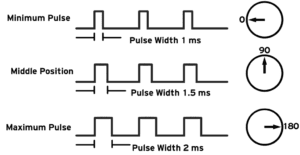
The angular rotation of the servo motor depends on the clock’s duty cycle (ON Period). As per the above diagram, we may see, that
- The minimum duty cycle of width 1 ms is subtending 0 degrees.
- The duty cycle of width 1.5 ms is subtending 90 degrees
- The maximum duty cycle of width 2 ms is subtending 180 degrees.

The Servo motor consists of a huge gear combination inside the motor with the potentiometer which decides the degree of the rotation of the motor. As you have read in the above-mentioned paragraph working of the servo motors. I hope you all understand the working, principle and many more things about the servo motors.