Hello Friends, Today I’m back with a very important basic article that you need while working in electronics and electrical devices. First I want to make it clear that I’ll cover all the semiconductors topics like diodes, PN-junction, Rectifiers, Zener, and others but in the series, all further article links will be provided at the end of each.
So this article may be a bit long but will be very informative. Also, if you are interested in basic topics like this, then read them BASIC ELECTRONICS. Moreover, for articles related to Arduino and Raspberry Pi, visit the provided links. Now let’s get started.
SEMICONDUCTORS
- These are the devices which do-not conduct in ordinary conditions like other conductors do but become conductive when increasing or decreasing temperature, ,electricity, light and etc. or doping with some other material.
- In early times like when vacuum tubes were used, those were also called semiconductors, but the difference exists between modern semiconductors devices in those one.
- The medium through which the conduction of electrons takes place is the difference, in vacuum tubes it takes place through Gaseous while in modern semiconductors it takes place in solid form or through surface.
- Silicon and Germanium are the basic semiconductors known, apart from this their doped semiconductors are also used now-a-days.
Types of Semiconductors
Intrinsic
- Silicon (Si) & Germanium(Ge) are the type of Intrinsic semiconductors
- At low temperature they do not have free electrons, but on increasing temperature they begin to conduct due to release of free electrons and holes.
- As on increasinf tempreature the bonds between Silicon & Germanium breaks relasing electrons into holes and hece they become conductive.
Extrinsic
These semiconductors are also called Impure semiconductors, as they are doped with other materials to form P-type or N-type semiconductors.
N-Type
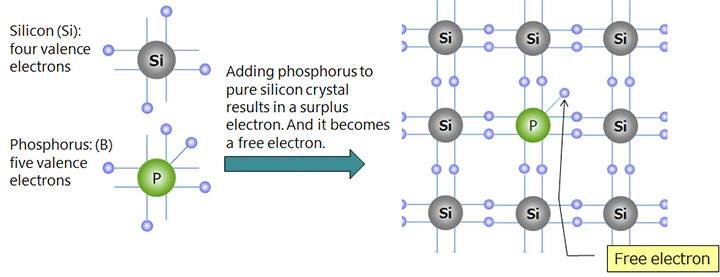
- These are semiconductors in which electrons are majority charge carriers and holes are minority charge carriers.
- When few atoms of elements like arsenic are doped into pure silicon or germanium, n-type semiconductor is formed.
- This doping results in release of electrons which significantly increase the number of electrons then number of holes.
P-Type
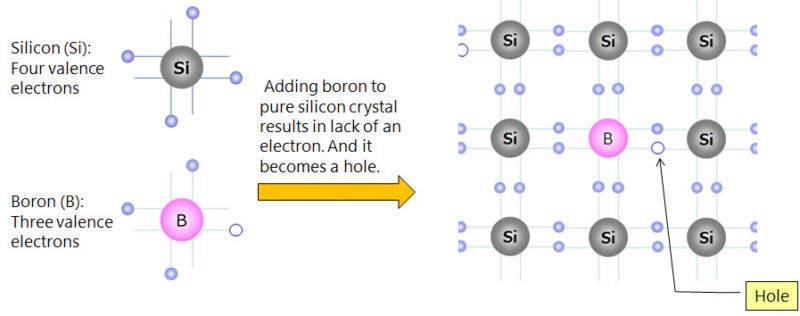
- In these semiconductors, holes are majority charge carries and electrons are minority charge carriers.
- When atoms like Boron(B) & Aluminum(Al) are doped with pure Silicon or germanium, P-type semiconductor is formed.
- Boron and Aluminum accepts electrons, hence significantly decrease the number of electrons then number of holes.
With this the part of the semiconductor has been completed, in the next article, we’ll discuss Diodes and P-N Junction. Until then enjoy these types of articles and if you need any other information comment down, I’ll add them.
