Hey guys, Welcome back to Techatronic. we are here with another informatic article. Today’s topic is very important if you are an electronic student. we will discuss what is a transistor. The name transistor is very common in the Electronics field. This gonna be the complete article read the full article we will share all the information as we have shared in the title. before we have covered some basic topics in the last articles such as What is a circuit and voltage. So now this is the next article to learn basic electronics. Here we will cover what is transistors, the types of transistors, their uses, applications, and much more. so, let’s get started.
Semiconductors are one of the vital parts of the vast majority of the electronic gadgets that are available today. Created in the year 1947 by three American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the semiconductor is considered as perhaps the main development throughout the entire existence of science.

Table of Contents
What is a Transistor?
The transistor is a semiconductor device that is widely used in electronics. this is basically the combination of two diodes. the transistor is used to amplify or switch electronic signals also the electrical power. These are basic building blocks in any modern electronics. It is made of semiconductor material they have three terminals usually with these Terminals we can connect the electronic hardware. So here this paragraph can refer to what is a transistor?. the transistor can conduct or insulate the current. due to this property, the transistor uses widely. there is two common use of the transistor are switch and amplifier. which helps a lot in any circuit.
usually, a transistor is made of three layers of semiconductor materials or then again more explicitly terminals which help to make a path with an outer circuit and convey the current. A voltage or current that is applied to anybody pair of the terminals of a semiconductor controls the current through the other pair of terminals. There are three terminals for a semiconductor. They are;
- Base:- this is also known as the gate of the transistor which helps to activate the current flow.
- Collector:- it is the path to convey the current with the emitter.
- Emitter: Emitter is another corner path that will be completed after the base activated.

How does the transistor works| working of transistor?
To understand the working and application of the transistor we need to learn both PNP and NPN transistor working. when the electrons and the holes start moving between the n-type and p-type semiconductors across the two junctions. There we need a small current at the base that can turn on a big current flow between the emitter and the collector. So, the base is responsible for switching the whole transistor on and off.
PNP Transistor working
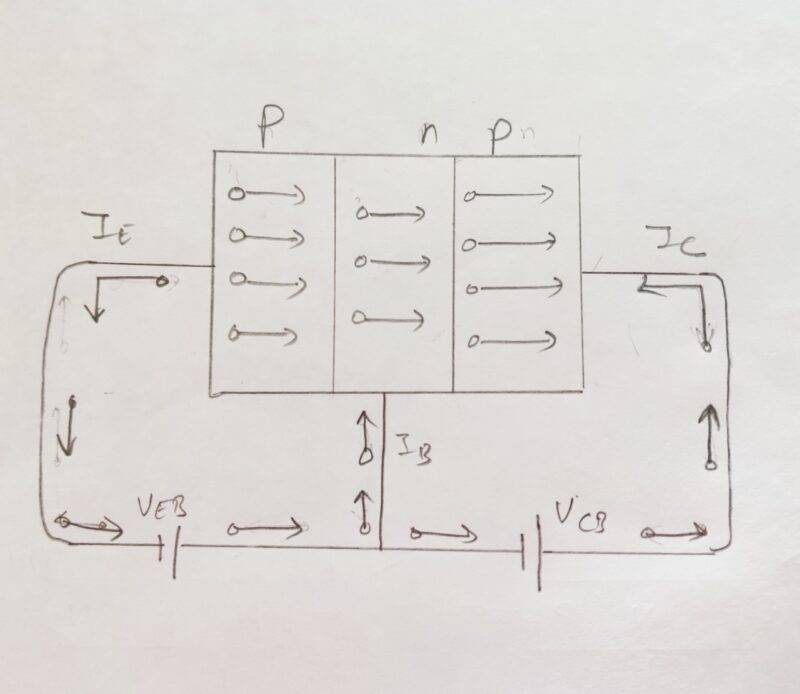
PNP-type transistors contain two P-type semiconductor materials and an n-type semiconductor material. N-type material sandwiched between the two p-type materials. so, there they made 2 junctions where the electrons move across the junctions. In PNP transistors there are two p-n junctions made. and on these both on the junction naturally a potential barrier created by the abundant electrons whose are free to move. these free electrons move towards the holes of another region.


so, in the same region, they created a positive charge by losing their region and making a negative charge in another region where they reached now. so one side is a positive charge and at the other side is a negative charge so this makes a potential barrier at the junctions for this PNP transistor. Now if we applied the batteries at both ends of the transistor it means at the emitter and the collector. then there is one forward biased and one reverse biased diode which result doest not flow any current through the end. but if we applied a negative terminal of the battery at the base too then both junctions will be forward biased and start a huge amount of current flow from collector to emitter.
NPN Transistor working
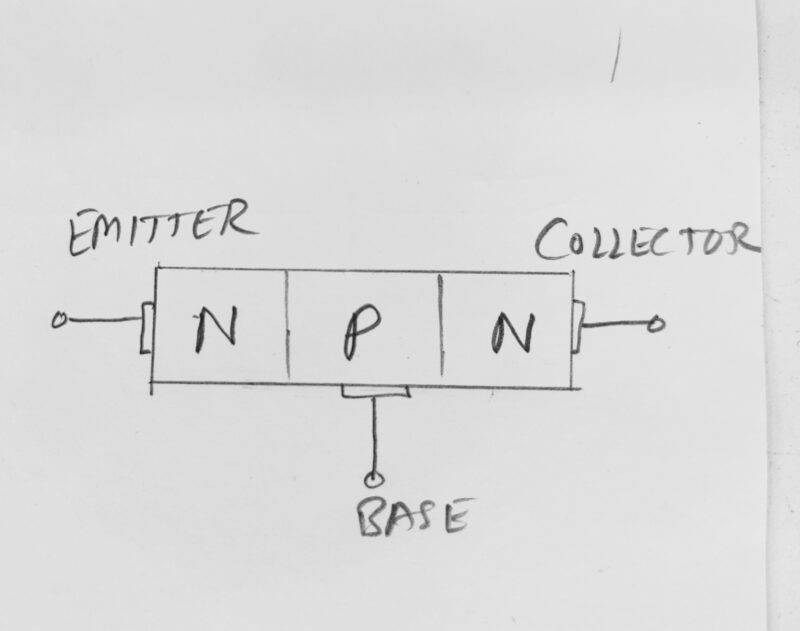
NPN-type transistors contain two N-type semiconductor materials and a P-type semiconductor material. P-type material sandwiched between the two N-type materials. so, there they made 2 junctions where the electrons move across the junctions. In NPN transistors working there are two p-n junctions made? and on these both on the junction naturally a potential barrier created by the abundant electrons whose are free to move. these free electrons move towards the holes of another region.

so, in the same region, they created a positive charge by losing their region and making a negative charge in another region where they reached now. so one side is a positive charge and at the other side is a negative charge so this makes a potential barrier at the junctions. Now if we applied the batteries at both ends of the transistor it means at the emitter and the collector.
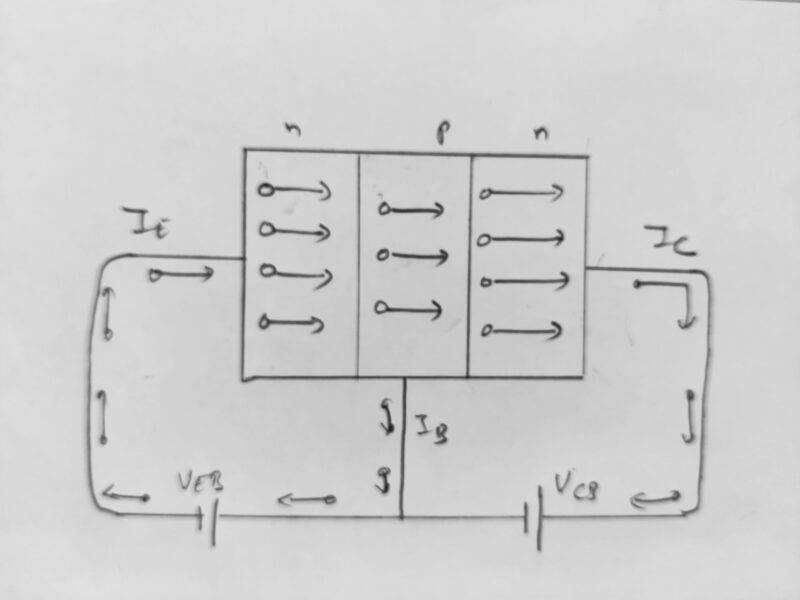
then there is one forward biased and one reverse biased diode which result doest not flow any current through the end. but if we applied to give a path to electrons to small current(positive) at the base then from the P region electrons comes towards the positive terminal of the battery which makes the holes in the p region that attract the electrons from the n region and these 99 % electrons flow from the emitter to collecter this result a huge amount of current flow from collector to emitter.
Types of Transistors!
Transistors are differentiated according to the material and doping. There are many types of transistors available in the market such as BJT, FET. we will learn more about this transistor below.
BJT:- Bipolar junction transistor
BJT have further two type NPN & PNP. we have shared a detailed description above on both.
FET:- Field effect transistor
For FET, the three terminals are Gate, Source, and Drain. The voltage we provide at the gate terminal can control current flows from the source and drain. FET is a unipolar transistor in which N channel FET or P channel FET are used for conduction. The main applications of FETs are low noise amplifiers, buffer amplifiers, and analog switches.
Uses of Transistors.
so, there is a lot of application of transistor, some of the applications we are giving in the following paragraph.
- switching applications and amplification.
- There is a kind of transistors that produce current flow depending on the amount of light incident upon them, those are known as phototransistors.
- Logic Gates
- To make memories
- In Microcontroller
- Mobile phones, TV, radio, and almost every electronic gadget.

