Hello Tech folks, Today we’re going to discuss another article on basic electronics. Transformers are an important component when working with electronics. You may seem this to be confusing, but it is true. Transformers are used in various aspects of electronics either to deliver power, convert voltages (large difference), Amplifiers, etc. They are rather simple to work with and understand if carefully learned about. So let’s start.
What is Transformer?
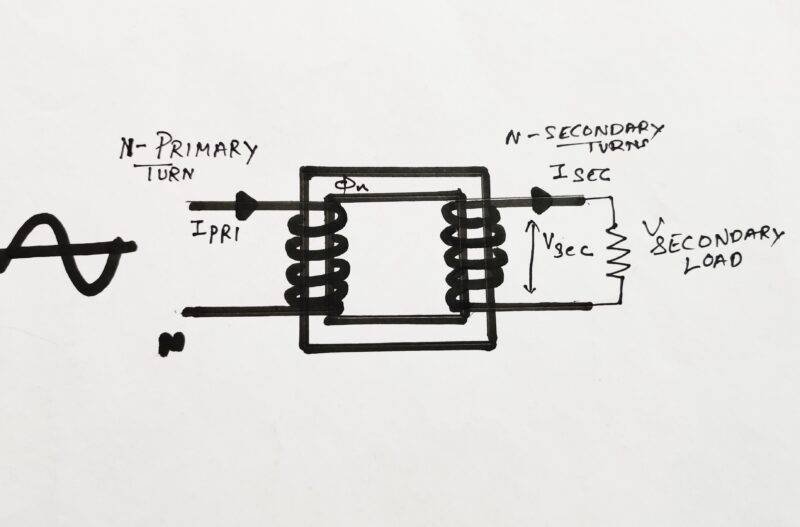
so, here we are explaining what is a transformer. A transformer is a device that is used to convert voltages either from high to low or vice versa. Also, they come in various types according to their construction and need for the circuit. We’ll discuss it in a later part, for now, let’s understand some of its basic concepts. The very basic transformer which is used in Power adapters, SMPS, and other AC devices mainly built out of 2 Coils or windings. These two windings either can be used to step up a voltage or to step down voltage. to understand what is a transformer you need to read the full article carefully. .
The primary coil is the main coil in which we supply voltage or power through AC. It can be used in Ac only because to induce a current in secondary it needs change in a magnetic field which is a bit complicated in DC source. The primary coil of the transformer is built of more number coils or thick wire to induce a high magnetic field and hence flux which is passed through the core of the Transformer and finally to the secondary coil. Which induces EMF in the secondary coil and hence induces a current.
Core behaves as the main part in the construction of Transformer they are either air-cored, iron cores or some ferrite material core. In the Adapter in our house, mainly Ferrite cores are used as it does not need much amount of power to be delivered. But in devices like Inverters or Amplifiers, iron cores are used to enhance the efficiency of the Transformer. In Large power Transformer-like which is used to deliver electricity to our houses, Air core is used along with oil cooling to dissipate heat generated.
How does Transformer works?
Transformer works on the principal Faraday’s law of electromagnetic Induction. s, here the full working of transformer is totally dependent on the mutual induction principle. I hope you might be remembering this topic from your lower classes. Yes, it is a topic in +2 classes in my case. At that time, practical implementation was a bit difficult due to the lack of availability of resources. EMI and electromagnetism are described in another article which you can read to understand for more clearance. The electromagnetic flux created by the primary coil is passed through the core to the secondary coil to induce EMF in it. Some basic relation between I, V, and N(turns)
I1/I2=N1/N2 V1/V2=N1/N2
using these formulas, you can calculate any of the assuming values for basic purposes.
Types of transformer:
There are basically two types, which are classified as per the requirement. Transformers are the device which use to transform the energy either is low to high or from high to low. according to this, there are only two types of transformer which are given below.
STEP-DOWN TRANSFORMER
These types of transformers are used in power adapters or supplies to convert high voltage to a low voltage but work only with AC power. As the power is in AC now also, it needs to be converted into DC using a Full bridge rectifier which converts AC into DC. Also, due to some reasons, we need to purify or filter the incoming and outgoing current at input and output for that purpose we generally use Capacitors of the same voltages as input & output or some and around 100-2000 µF. This circuit is basically meant for drawing less power in adapters but in SMPS due to a large amount of power Iron cored transformers with feedback circuit is used to make circuit and power transformation more efficient.
STEP-UP TRANSFORMER
These types of transformers are used in amplifying or inverter circuits. Sound amplifiers of high quality or more advanced ones use Step up Transformation for sound amplification as it is more efficient rather than using some sort of ICs. Also in inverter circuits and like Home inverters or UPS this step-up transformer is used but with an iron core to deliver more power at the output as the output will be in AC. In inverters, a sine wave inverter is used to convert DC into AC but in audio amplifiers either sine wave inverter is used if it runs on DC but if it runs on AC also it didn’t need a sine wave inverter.
Losses & Efficiency:
There are large numbers of types of losses in transformers, some of which are listed below.
Losses in Transformer
Core loss of hysteresis loss:
Due to high usage and large time usage of transformers in circuits, the core came through very rapid change in flux and hence the rapid change in magnetization and demagnetization. Due to this after some time it starts losing its ferrite properties and results in loss of power and efficiency. Also, Eddy currents developed during transformation results in loss of power
Copper loss:
As the coils are generally made up of copper wire which will definitely have some resistance. Due to this resistance, heat is generated during transformation, and power is lost in the form of heat. To reduce heat to too much extent copper wires are used in place of thin to reduce resistance as much as possible. And hence reducing power loss in the form of heat
Transformer Efficiency:
Efficiency is nothing just but the percentage of the ratio of power input to the power output. Basically, it is used to check or compare different transformers and their construction.
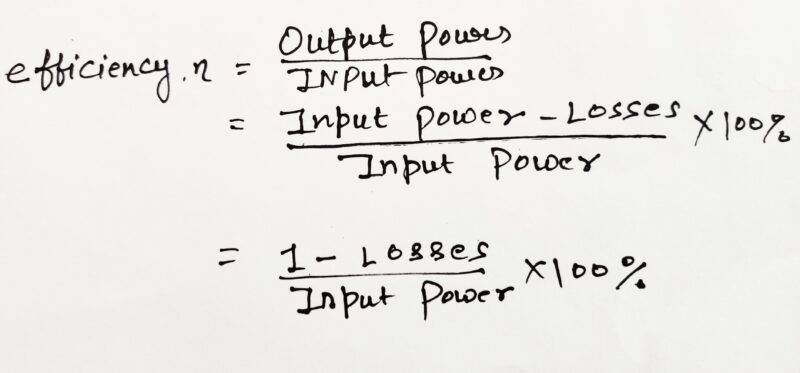
╖(Efficiency)=Power Output x 100/Power Input
With this, we have completed our basic electronics article on transformers. I hope you like it, for any other information let me know below.